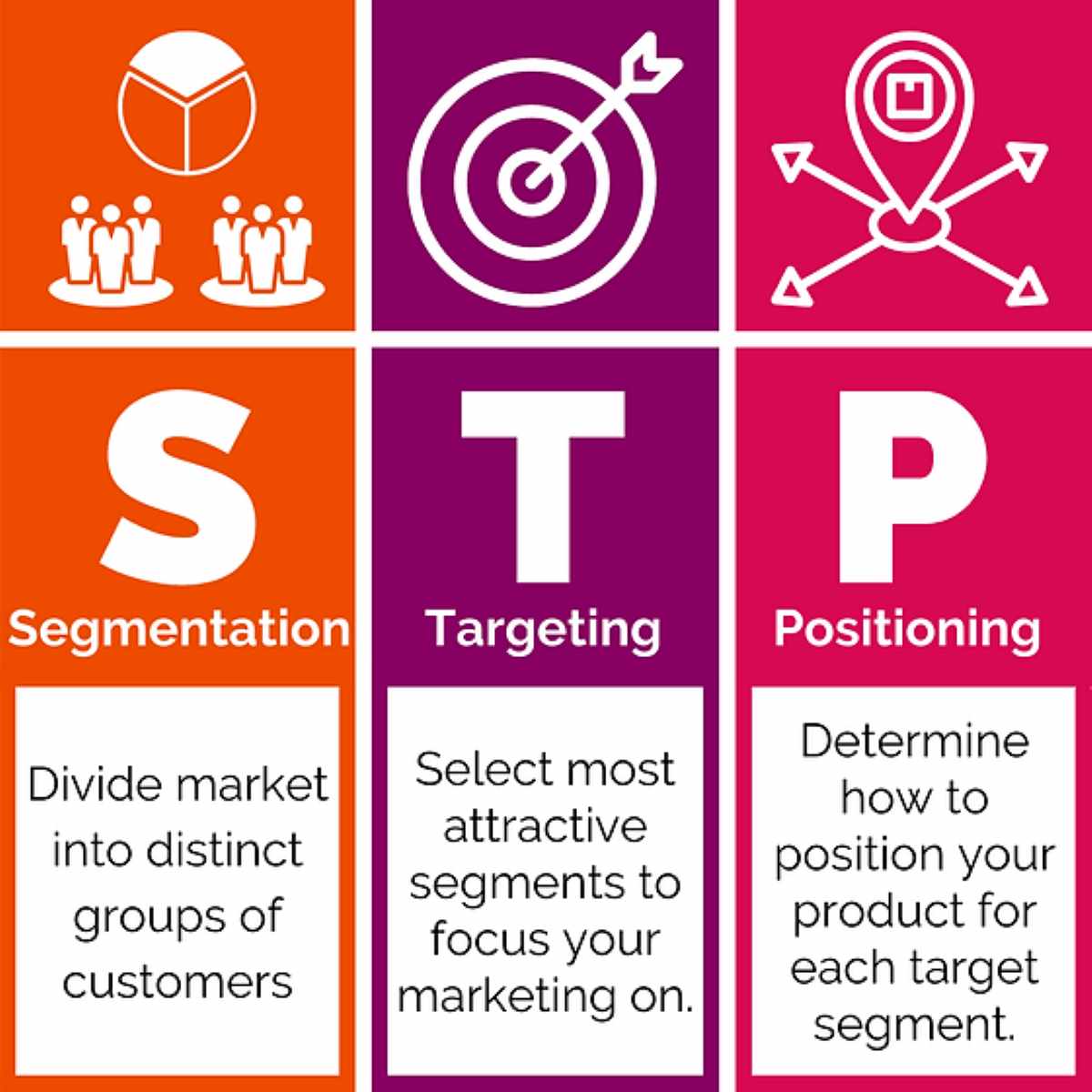
Understanding the STP Marketing Model
Delivering a business's message to the right audience is crucial for success. The STP marketing model—Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning—offers a structured approach to achieve this goal. This strategy helps companies identify their most relevant customers, focus their marketing efforts on these groups, and ensure their brand stands out in a competitive landscape.
The First Step: Segmentation
The first step in the STP process is segmentation. This involves dividing the broader market into smaller, more manageable groups based on various factors such as age, gender, preferences, and lifestyle choices. Customers with similar needs and behaviors are grouped together to create distinct market segments. These segments are parts of the larger market that are likely to respond similarly to specific marketing initiatives.
Segmentation allows businesses to pinpoint which customer types are most suitable for their products or services. It is essential to carry out this process carefully to avoid wasting resources. Common ways to segment a market include:
- Psychographic traits (lifestyle and personal values)
- Geographic attributes (location-based considerations)
- Behavioral traits (buying habits and usage patterns)
- Demographic factors (age, gender, income level)
Once the market is segmented, companies can select the most appropriate group to focus on, ensuring efficient use of time and budget.
The Second Step: Targeting
After segmentation, the next stage is targeting. This involves analyzing different market segments to determine which one aligns best with the company’s offerings. Targeting identifies the ideal audience and assesses the size of the market that can be reached.
In simple terms, it is the process of choosing the most suitable audience for a product or service while excluding others who may not be interested. Businesses must conduct thorough research to understand their target audience effectively. Otherwise, they risk investing time and money without achieving a satisfactory return on investment.
A new product or service is often introduced to a specific target market first. If successful, the business can then expand to other markets. The size of the business also influences how it targets its audience, as the cost of targeting increases with the number of segments being addressed.
The Final Step: Positioning
Positioning is the final stage of the STP model. It involves placing the product or service in the minds of the target audience in a way that makes it more appealing than competitors. Several factors influence this process:
- A larger target market can make positioning more challenging.
- If there is no competition, a business might develop a completely new positioning strategy.
- A strong brand value can make it easier to position new products or services.
- Offering lower prices than competitors can provide a competitive advantage.
Steps to Implement the STP Marketing Process
To effectively apply the STP model, businesses can follow these steps:
Step 1: Define the Market
Start by identifying a niche within the global market. Consider factors like the total available market (TAM), the serviceable available market (SAM), and the serviceable obtainable market (SOM). These metrics help determine the overall market size, the segment suitable for your product or service, and the portion you can realistically target.
Step 2: Map the Targeted Groups
Once the market is defined, further segment it using criteria such as age, income, location, interests, lifestyle, and behavior. The more detailed the analysis, the more precise the audience segments become.
Step 3: Create Profiles for Each Segment
Develop detailed profiles for each market segment. These should include their needs, behaviors, demographics, brand preferences, and shopping habits. This will help compare segments and choose the most suitable ones for marketing efforts.
Step 4: Assess the Attractiveness of Segments
Evaluate the potential of each segment by comparing market research results with customer studies. Consider factors such as size, growth rate, price sensitivity, and customer commitment. Identify segments with the highest potential for a strong return on investment.
Step 5: Choose Your Target Audience(s)
Select the audience(s) that best align with your business strategy and objectives. Take into account the size of the segment, level of competition, and growth potential.
Step 6: Plan Your Positioning Strategy
Determine what makes your business unique and how it will appeal to the target audience. This could involve offering a better alternative, fulfilling specific customer needs, introducing something novel, or highlighting the benefits of your product or service.
Step 7: Select Your Marketing Mix
Finally, implement your STP marketing plan by developing a marketing mix that aligns with your brand’s position. This includes elements such as product features, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and promotional activities.
Conclusion
The STP marketing model enables businesses to better understand and connect with their customers. By dividing the market into smaller segments (Segmentation), focusing on the most significant groups (Targeting), and ensuring their products or services appeal to these groups (Positioning), companies can stand out from competitors and achieve long-term success.
